The Asian Development Bank (ADB) has announced new and more concessional lending terms for small island developing states.
This concessional capital lending terms is to support SIDS in its efforts to meet infrastructural needs, strengthen social services, and scale up investments in climate adaptation and disaster risk reductions.
The new lending terms, which took effect on October 1, 2023, represent the most concessional financing available from ADB, aside from grants.
The terms include a 1 per cent interest rate, a 10-year grace period, a 40-year maturity, and principal repayments of 2 per cent a year for the first 10 years after the grace period and 4 per cent a year, thereafter.
The ADB anticipates the new terms to help reduce future debt service obligations of SIDS, “which have seen eroding fiscal space and rising debt burdens due to the lingering impacts of the pandemic and subsequent global shocks”.
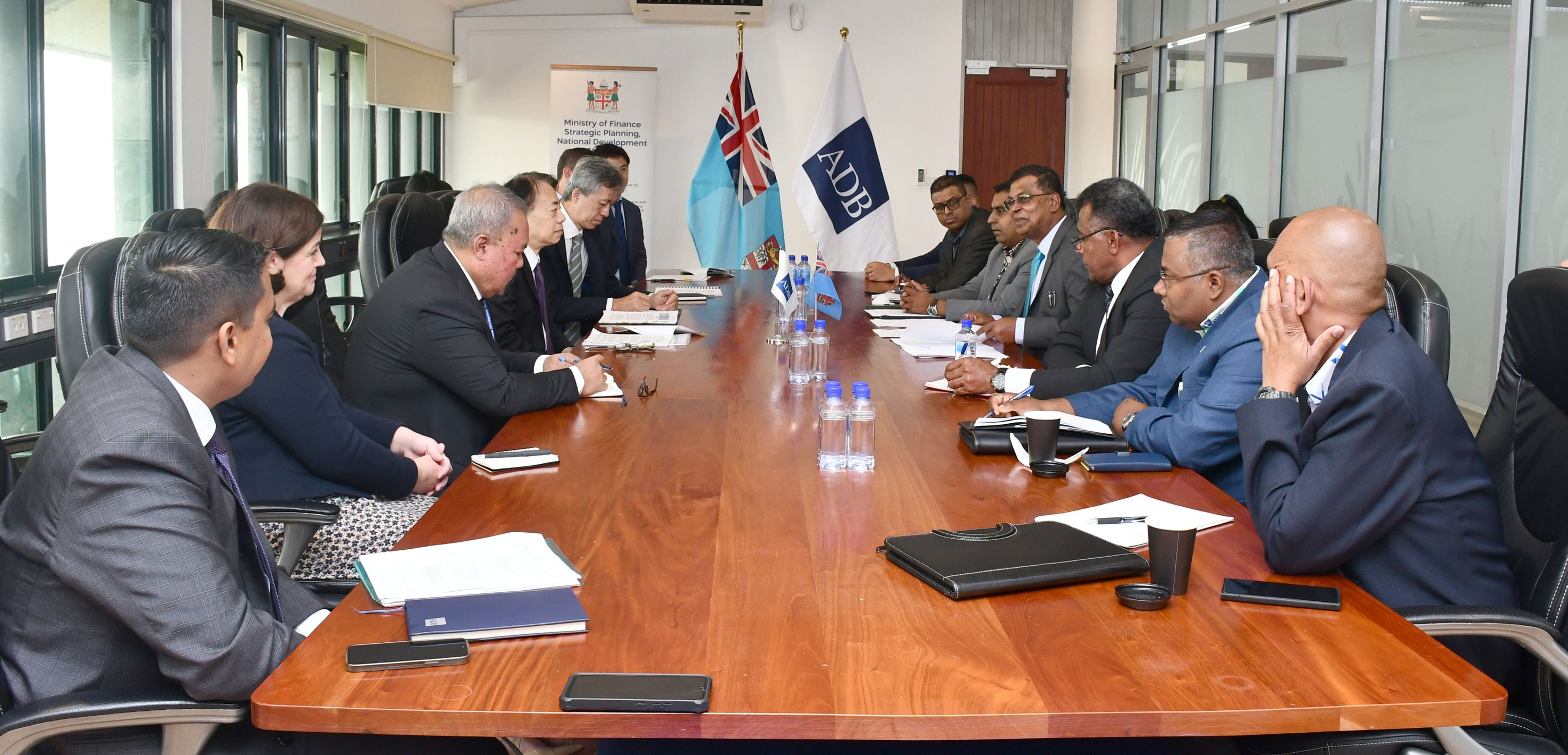
ADB president Masatsugu Asakawa made the announcement in Suva, Fiji, during a meeting with the island nation’s deputy Prime Minister and Minister for Finance Professor Biman Prasad.
“ADB is a long-standing partner in development with the Pacific and is committed to continuously refining its differentiated approach to helping SIDS build resilience amid intensifying vulnerabilities,” Mr. Asakawa said in a statement from the ADB.
“This significant improvement in concessional lending terms will help SIDS ramp up critical investments, including for climate operations and other global and regional public goods.”
With these changes, all ADB SIDS members are eligible for highly concessional funding or grants.
Fiji, Vanuatu, Solomon Islands, Papua New Guinea, Cook Islands, Niue, Palau, and Timor-Leste are eligible for the concessional ordinary capital resources lending.
Solomon Islands and Vanuatu are also eligible for grants from the ADB, which provides grants to ADB’s poorest and most vulnerable developing member countries, along with the Federated States of Micronesia, Kiribati, Maldives, the Marshall Islands, Nauru, Samoa, Tonga, and Tuvalu.
ADB is committed to achieving a prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable Asia and the Pacific, while sustaining its efforts to eradicate extreme poverty.
The ADB was established in 1966, and it is owned by 68 members—49 from the region.