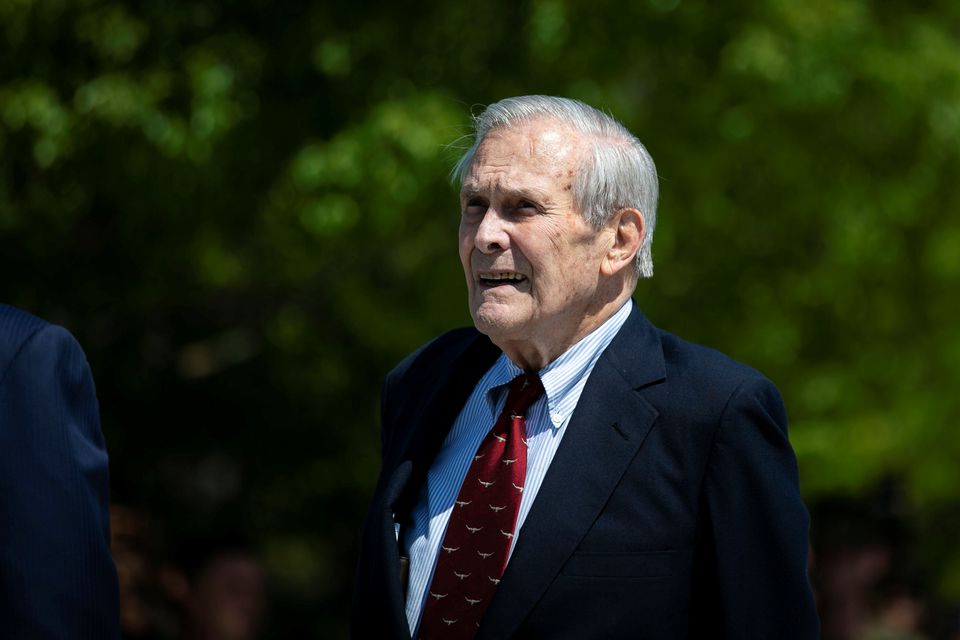
June 30 – Donald Rumsfeld, a forceful U.S. defense secretary who was the main architect of the Iraq war until President George W. Bush replaced him as the United States found itself bogged down after 3-1/2 years of fighting, has died at age 88, his family said in a statement on Wednesday.
“It is with deep sadness that we share the news of the passing of Donald Rumsfeld, an American statesman and devoted husband, father, grandfather and great grandfather,” the statement said. “At 88, he was surrounded by family in his beloved Taos, New Mexico.”
The statement did not say when Rumsfeld died.
Rumsfeld, who ranks with Vietnam War-era defense secretary Robert McNamara as the most powerful men to hold the post, brought charisma and bombast to the Pentagon job, projecting the Bush administration’s muscular approach to world affairs.
With Rumsfeld in charge, U.S. forces swiftly toppled Iraqi President Saddam Hussein but failed to maintain law and order in the aftermath, and Iraq descended into chaos with a bloody insurgency and violence between Sunni and Shi’ite Muslims. U.S. troops remained in Iraq until 2011, long after he left his post.
Rumsfeld played a leading role ahead of the war in making the case to the world for the March 2003 invasion. He warned of the dangers of Iraqi weapons of mass destruction but no such weapons were ever discovered.
Only McNamara served as defense secretary for longer than Rumsfeld, who had two stints – from 1975 to 1977 under President Gerald Ford, for whom he also served as White House chief of staff, and from 2001 to 2006 under Bush.
Rumsfeld was known for imperious treatment of some military officers and members of Congress and infighting with other members of the Bush team, including Secretary of State Colin Powell. He also alienated U.S. allies in Europe.
In 2004, Bush twice refused to accept Rumsfeld’s offer to resign after photos surfaced of U.S. personnel abusing prisoners at the Abu Ghraib prison outside Baghdad. The scandal triggered international condemnation of the United States.
The United States faced global condemnation after the photos showed U.S. troops smiling, laughing and giving thumbs up as prisoners were forced into sexually abusive and humiliating positions including a naked human pyramid and simulated sex. One photo showed a prisoner forced to stand on a small box, his head covered in a black hood, with wires attached to his body.
Rumsfeld personally authorized harsh interrogation techniques for detainees. The U.S. treatment of detainees in Iraq and foreign terrorism suspects at a special prison set up under Rumsfeld at the U.S. naval base at Guantanamo Bay, Cuba, drew international condemnation, with human rights activists and others saying prisoners were tortured.
He was a close ally of Bush’s vice president, Dick Cheney, who had worked for Rumsfeld during the 1970s Republican presidencies of Richard Nixon and Ford.
Rumsfeld became a lightning rod for criticism and, with the Iraq war largely a stalemate and public support eroding, Bush replaced him in November 2006 over Cheney’s objections.