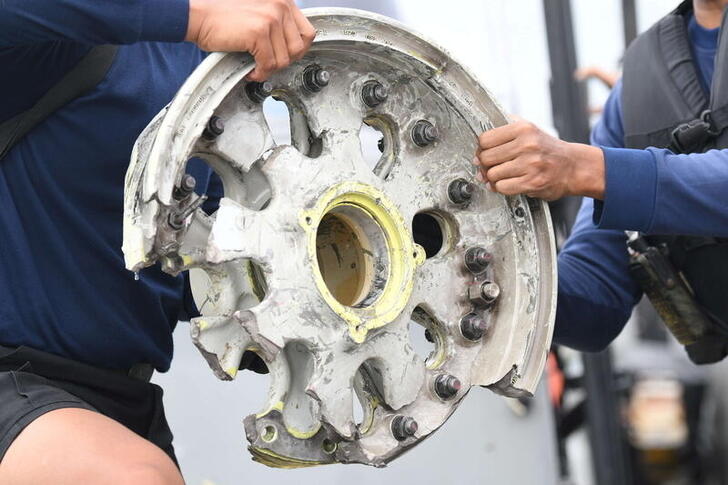
SYDNEY/JAKARTA (Reuters) – Indonesia’s chequered air safety record is again in the spotlight after a Sriwijaya Air jet carrying 62 people crashed into the Java Sea minutes after take-off on Saturday, marking the country’s third major airline crash in just over six years.
Before the crash there had been 697 fatalities in Indonesia over the last decade including military and private planes, making it the deadliest aviation market in the world – ahead of Russia, Iran and Pakistan – according to Aviation Safety Network’s database.
The Sriwijaya crash of a Boeing Co 737-500 follows the loss of a Lion Air 737 MAX in October 2018 that contributed to a global grounding of the model and the crash of an AirAsia Indonesia Airbus SE A320 in December 2014.
The Lion Air crash, which killed 189 people, was an outlier in that it mainly revealed fundamental issues with the plane model and triggered a worldwide safety crisis for Boeing. Even excluding the deaths from that crash, Indonesia would rank above Russia if there are no survivors from Saturday’s crash.
Indonesia, an archipelago of thousands of islands, is highly dependent on air travel and its safety issues illustrate the challenge relatively new carriers face as they try to keep pace with unstoppable demand for air travel in developing nations while striving for standards that mature markets took decades to reach.
From 2007 to 2018, the European Union banned Indonesian airlines following a series of crashes and reports of deteriorating oversight and maintenance. The United States lowered its Indonesia safety evaluation to Category 2, meaning its regulatory system was inadequate, between 2007 and 2016.